|
|
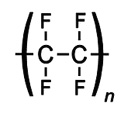
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene which finds numerous applications. |
| PTFE is a fluorocarbon solid, as it is a high molecular weight compound consisting wholly of carbon and fluorine. Neither water and water-containing substances nor oil and oil-containing substances are wet by PTFE. |
| PTFE is used as a non-stick coating for pans and other cookware. It is very non-reactive, partly because of the strength of carbon–fluorine bonds, and so it is often used in containers and pipe work for reactive and corrosive chemicals. Where used as a lubricant, PTFE reduces friction, wear and energy consumption of machinery. |
Polytetrafluoroethylene |
|
|
| PTFE is a white solid at room temperature, with a density of about 2.2 g/cm³. Its melting point is 327 °C (620.6 °F), PTFE gains its properties from the aggregate effect of carbon-fluorine bonds, as do all fluorocarbons. |
| PTFE has excellent dielectric properties. This is especially true at high radio frequencies, making it suitable for use as an insulator in cables and connector assemblies and as a material for printed circuit boards used at microwave frequencies. Combined with its high melting temperature, this makes it the material of choice as a high-performance substitute for the weaker and lower melting point polyethylene that is commonly used in low-cost applications. Its extremely high bulk resistivity makes it an ideal material for fabricating long life electrets, useful devices that are the electrostatic analogues of magnets. |
| A little bit of creep allows PTFE seals to conform to mating surfaces better than most other plastic seals. |
| PTFE (Teflon) sleeves and PTFE sealing rings have been used in between joints to fit them together instead of grease. |
| INDUSTRIAL USES |
| Smoke Hood Suspension, Hoisting Arrangement etc. |
| |
|
 |
|
|
|
 |